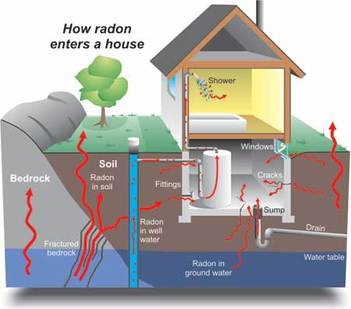
 Radon is a colourless, odourless gas that is produced naturally during the breakdown of uranium in the ground. It can make its way into your home and ultimately cause severe health effects including lung cancer. Outdoors, radon is dissipated quite easily and isn't a massive cause for concern. Indoors, however, radon can become trapped and levels will build to the point where they are a definite health risk. Radon can enter your home any place where the house touches the soil and there is an opening. For example, - cracks in foundation walls and floor slabs - construction joints - gaps around service pipes - support posts - window encasements - floor drains - sumps or cavities inside walls - dirt floors The amount of radon in your home depends on, - the amount of uranium in the ground - the number of entry points into your home - how well your home is ventilated HEALTH RISKS Radon exposure increases your risk of developing lung cancer. It is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. The combination of radon exposure and smoking significantly increases the chances of developing lung cancer. Another reason to quit. The other two main factors that will determine the effect on you will be, how long you are exposed to it, and the level of radon in your house. HOW TO DETECT RADON Although almost every home in Canada has some radon in it, the levels vary from one house to another. Even if they are next door to each other. Testing for radon in your home is simple and inexpensive. There are two options for testing. 1. Hire a certified radon measurement professional. 2. Do it yourself. You can purchase a home radon kit for between $30 and $60 from most large hardware stores. They can also be ordered online. The kits include a radon detector that is meant to be exposed to the air inside of your home and then sent to a lab for analysis. **Health Canada recommends that you use a long-term test device for at least three months. The best time is between September and April when the windows are mostly closed. REDUCING RADON IN YOUR HOME If the levels of radon in your home are above the Canadian guideline of 200 becquerels/meter cubed, you need to reduce it. The higher the level, the sooner it has to be reduced. A certified radon mitigation specialist can help to provide the most effective radon reduction solution. One of these more commonly used methods is sub-slab depressurization. A pipe is installed through the foundation floor and is piped to the outside with a small fan attached. The fan draws the radon laden air from under the house and pushes it back outside. This solution can reduce the radon in your home by more than 90%. Also, increased sealing and ventilation of radon entry points can also help to reduce levels, but these solutions may not be as effective as sub-slab depressurization. WHAT ABOUT CALGARY? Unfortunately us prairie folks are being effected by radon every day. According to Radon West, a Calgary based company, in Canmore, Banff, Okotoks and Calgary they are seeing 40% consistently of homes above the action level that Health Canada has set. Although Alberta is a hotspot for Radon, there is very low awareness at this point in time.
2 Comments
7/8/2014 10:47:00 am
Thank you so much for helping to educate the public about the danger of living, working, and attending school in environments with elevated levels of radioactive radon gas. Testing and fixing if the level is high is an easy way to save a life.
Reply
Sheri-Lee
7/9/2014 08:56:39 am
Thank you so much Gloria. There just isn't enough awareness yet, but we'll keep on talking about the dangers of Radon.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSheri-Lee Presenger Archives
January 2016
Categories
All
|
|
SHERI-LEE PRESENGER
Real Estate Agent Real Estate Professionals Inc #100, 5810 2nd Street SW Calgary, AB |
The data included on this website is deemed to be reliable, but is not guaranteed to be accurate by the Calgary Real Estate Board.
REAL POWER - REAL ESTATE

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed


